The Rise of Natural Medicinal Plants in Modern Healthcare
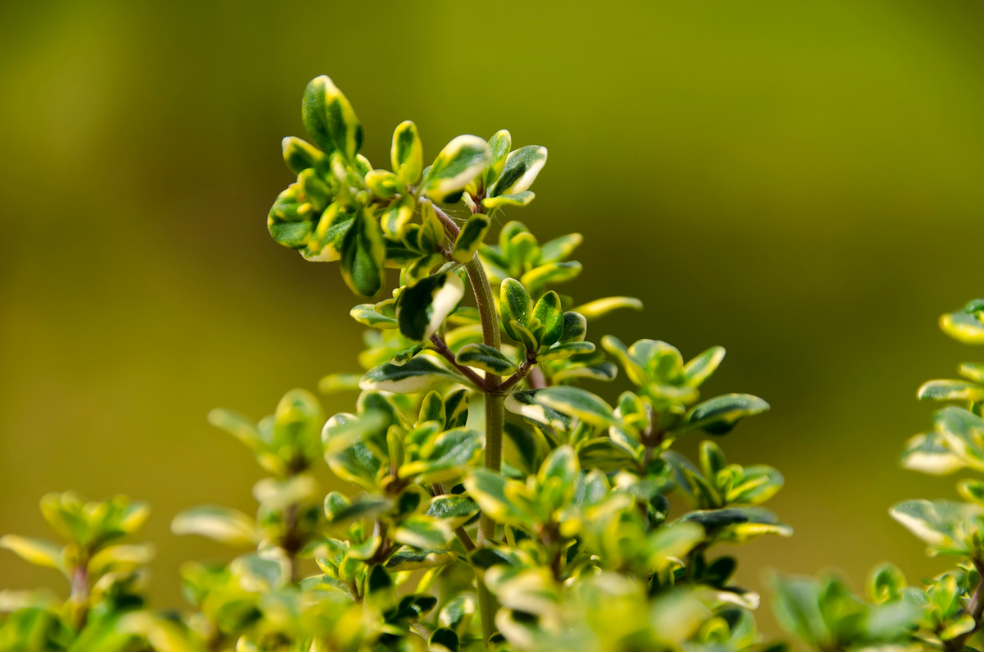
Medicinal plants from various countries have become increasingly popular and widely used as primary sources of treatment. As concerns about microbial resistance to antibiotics continue to rise, researchers are intensifying their studies on the antimicrobial properties of herbal plants to address this growing health issue. Thyme is used worldwide for culinary, cosmetic, and medicinal purposes. Its key active compounds, such as thymol and carvacrol, provide significant therapeutic effects. These compounds play an important role in thyme’s benefits for respiratory infections, including asthma and cough. Traditionally, thyme has been used to relieve respiratory conditions, reduce inflammation, and help open the airways—particularly in the treatment of cough and bronchitis across Europe.
How Thyme Helps Ease Respiratory Conditions
Asthma, an inflammatory disease marked by oxidative stress, is caused by a decrease in antioxidant activity. This results in reversible airflow obstruction and heightened airway sensitivity. Additionally, asthma is often linked to increased levels of Immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies, which cause an overreaction of the immune system to allergens. Thyme is highly regarded for its antispasmodic and broncholytic properties, making it an effective natural treatment for conditions like bronchitis, asthma, and whooping cough. In Central and Southern Europe, thyme has long been used to reduce mucosal inflammation in the respiratory tract and ease the symptoms of these respiratory ailments.
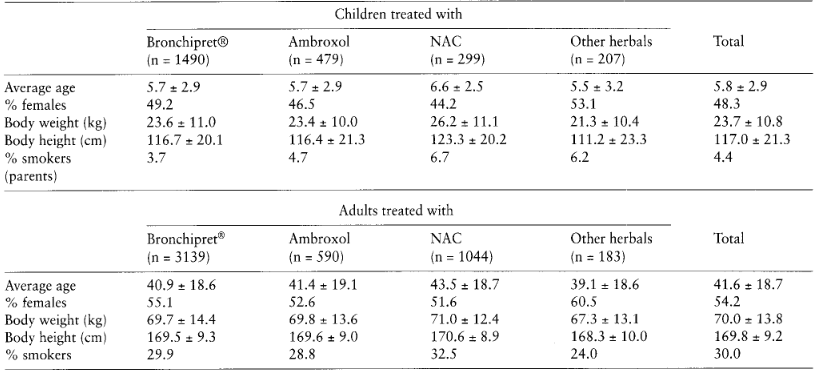
The compounds thymol and carvacrol have proven effective in stimulating mucus secretion and enhancing the movement of cilia in bronchial epithelia, which is essential for clearing mucus from the lungs. Research has shown that thyme’s therapeutic potential is particularly effective when combined with other herbal extracts. In one clinical study, a combination of thyme and Primulae radix in Bronchipret tablets outperformed other treatments, such as N-acetylcysteine and Ambroxol, in treating cough in both children and adults.
Mechanisms of Action Thyme Extract
The bronchodilatory effects of thymol and carvacrol contribute to their success in treating respiratory diseases. Thymol’s mechanism of action can be explored through its ability to act on the respiratory system via inhalation (nasal application), which has been shown to suppress coughing. Moreover, thymol has demonstrated antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making it beneficial for treating chronic respiratory conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. The ability of thymol to decrease inflammation in the airways and improve lung function has been supported by various studies, even though issues with dosage and delivery techniques still need to be further investigated.
Thyme as a Holistic Solution for Respiratory Health
Thyme exhibits unique effects on the immune system, with its active compounds—particularly thymol and carvacrol—helping regulate immune responses, reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine production, and support overall immune balance. These properties make thyme a natural remedy for respiratory infections such as asthma and cough, as it helps reduce inflammation, promotes bronchodilation, and enhances immune function, offering a holistic approach to respiratory health. Amid growing concerns about antibiotic resistance, thyme offers an effective and natural alternative for managing respiratory conditions, rooted in traditional remedies that have been used for over a century.
Source : Waheed, M., Hussain, M.B., Saeed, F., Afzaal, M., Ahmed, A., Irfan, R., Akram, N., Ahmed, F. and Hailu, G.G. (2024), Phytochemical Profiling and Therapeutic Potential of Thyme (Thymus spp.): A Medicinal Herb. Food Sci Nutr, 12: 9893-9912. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.4563








