Diabetes Mellitus: A Global Health Challenge
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to impaired insulin production or utilization. This condition has become a global health problem, with prevalence rates increasing each year. Therefore, the search for safe, effective, and natural therapies has become increasingly important.
One natural compound with great potential as an antidiabetic agent is andrographolide. This compound is isolated from the sambiloto plant (Andrographis paniculata), which has long been used in traditional medicine throughout Asia. In this article, we will discuss the potential of andrographolide as an antidiabetic agent based on recent research findings.
Andrographolide: The Active Compound of Sambiloto
Sambiloto (Andrographis paniculata) is a widely recognized medicinal herb known for its numerous health benefits, especially in traditional medicine. The primary active compound found in sambiloto is andrographolide, a diterpenoid lactone with significant pharmacological activities.
Andrographolide is known for its anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, hepatoprotective, and antimicrobial properties. Additionally, it shows promising antidiabetic potential, drawing the attention of researchers for further investigation.
(Astuti et al, 2022)
Mechanism of Action of Andrographolide as an Antidiabetic Agent
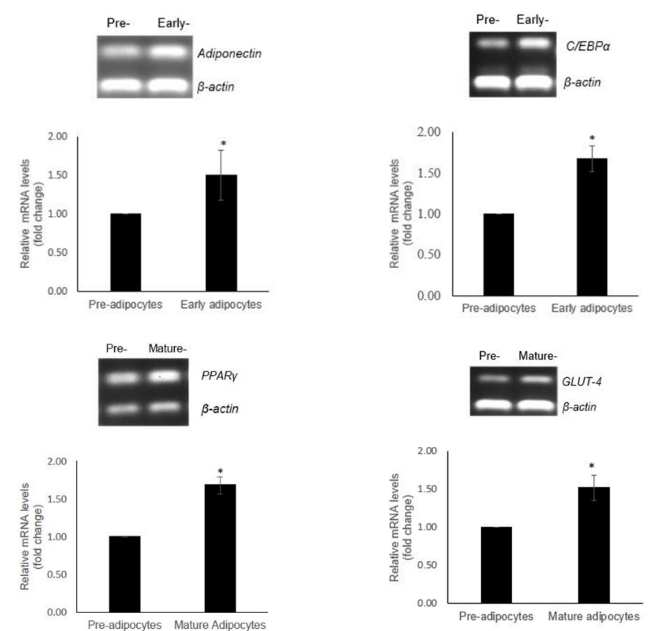
Recent studies have shown that andrographolide can enhance glucose uptake in fat cells (3T3-L1 adipocytes). This effect occurs through increased expression of two crucial proteins involved in glucose metabolism:
PPARγ (Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma)
– Plays a role in adipocyte differentiation and regulation of lipid and glucose metabolism.
– Activation of PPARγ increases insulin sensitivity and facilitates glucose uptake by adipose tissue.
GLUT-4 (Glucose Transporter Type 4)
– A transporter protein responsible for moving glucose from the bloodstream into cells, primarily in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle.
– Increased GLUT-4 expression helps maintain stable blood glucose levels.
By enhancing the expression of PPARγ and GLUT-4, andrographolide demonstrates significant potential as an antidiabetic agent, whether in the form of herbal extracts or natural-based pharmaceutical products.
Potential Product Development
Given the effectiveness of andrographolide in promoting glucose uptake, there are promising opportunities for developing herbal antidiabetic products. In addition to nutraceutical supplements, sambiloto extract can be formulated as standardized herbal medicines to support natural diabetes management.
The primary advantage of using natural compounds like andrographolide lies in their reduced side effects compared to synthetic drugs. This makes them an attractive alternative for safer and more body-friendly therapies.
Conclusion
Andrographolide, the active compound derived from sambiloto, offers a new hope in diabetes therapy through its mechanism of increasing PPARγ and GLUT-4 expression. With ongoing research, the potential utilization of sambiloto extract as an antidiabetic agent continues to strengthen.
Utilizing herbal ingredients as health solutions is a wise step to reduce dependence on synthetic drugs and improve the quality of life for people with diabetes. Therefore, continued support for research and clinical trials is essential to ensure that the benefits of andrographolide can be widely applied in the medical field.
Source :
Astuti, N. T., Novitasari, P. R., Tjandrawinata, R., Nugroho, A. E., & Pramono, S. (2022). Anti‐diabetic effect of andrographolide from Sambiloto herbs (Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Nees) through the expression of PPARγ and GLUT‐4 in adipocytes. Indonesian Journal of Biotechnology, 27(4). https://doi.org/10.22146/ijbiotech.68800








